As the summer approaches and the UV index rises, it’s important to remember that tanning safely requires taking precautions to protect your skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. Here are some tips for sun tanning safely:
Use Sunscreen
Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
Time Your Exposure
Avoid the sun during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) when UV rays are strongest. Aim for shorter tanning sessions outside these hours.
Gradual Exposure
Start with short periods in the sun and gradually increase your exposure time to prevent burning.
Protect Sensitive Areas:
Use extra protection for sensitive areas like your face, ears, and shoulders. Wear a wide-brimmed hat and UV-protective sunglasses.
Hydrate:
Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated. Dehydration can make your skin more susceptible to damage.
Seek Shade
Take breaks in the shade to give your skin a rest from direct sunlight.
Moisturize
After tanning, use a good moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated and help repair any damage.
Monitor Your Skin
Keep an eye on any changes in your skin, such as new moles or changes in existing ones, and consult a dermatologist if you notice anything unusual.
What’s The Difference Between Sunscreen and Sunblock?
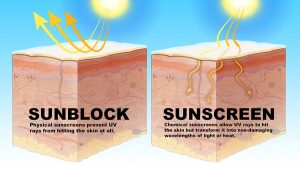 Sunblock and sunscreen both protect the skin from harmful UV radiation, but they work in different ways and contain different ingredients. If you want to safely tan, you can use sunscreen. It keeps your skin safe while also giving you a tan because no sunscreen can block 100% of the sun’s UV rays and this enables you to tan while wearing it. Sunblock, on the other hand, doesn’t absorb UV rays– it deflects them from your skin, so getting a tan with sunblock is a lot harder than with sunscreen.
Sunblock and sunscreen both protect the skin from harmful UV radiation, but they work in different ways and contain different ingredients. If you want to safely tan, you can use sunscreen. It keeps your skin safe while also giving you a tan because no sunscreen can block 100% of the sun’s UV rays and this enables you to tan while wearing it. Sunblock, on the other hand, doesn’t absorb UV rays– it deflects them from your skin, so getting a tan with sunblock is a lot harder than with sunscreen.
Sunblock:
- Physical Barrier: Sunblock physically blocks or reflects UV radiation away from the skin. It often contains mineral ingredients such as zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
- Immediate Protection: It starts working immediately upon application since it sits on top of the skin.
- Opaque and Thicker: Sunblock is usually thicker and more opaque, which can leave a visible white or colored residue on the skin.
Sunscreen:
- Chemical Barrier: Sunscreen absorbs UV radiation and then transforms it into heat, which is then released from the skin. Common active ingredients include oxybenzone, avobenzone, octocrylene, and octinoxate.
- Needs Time to Work: Sunscreen typically needs to be applied about 15-30 minutes before sun exposure to be effective.
- Clear and Thinner: Sunscreen tends to be less visible on the skin and is generally thinner and easier to rub in.
UV Protection:
- Sunblock: Generally effective at protecting against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Sunscreen: Formulated to protect against UVA and UVB rays, but it’s important to choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen to ensure comprehensive protection.